Why?
Unlike earlier generations where we hardly saw 1 or 2 PCOS cases for every 100 women, PCOS has now turned into an epidemic with 1 in every 10 women suffering from the condition.
PCOD often starts without any symptoms and is found incidentally in most of the cases. 50% of PCOD cases go undiagnosed. Nevertheless, it is not something to be brushed aside as some women may be at risk of developing endometrial carcinoma with existing PCOD.
What is PCOD?
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a generic description for a broad spectrum of clinical and morphological finding in women with an endocrine (hormones secreted into the blood by glands) dysfunction and metabolism. Simply said it is a cluster of symptoms and anatomical findings which are due to hormonal and metabolism imbalance.
PCOD Hormonal aspect:
In PCOD – The glands in the brain don’t produce enough GnRH in normal cycles. It causes LH (Luteinising hormone) levels to rise, and FSH (Follicular stimulating hormone) levels to drop. LH causes ovary to produce more testosterone and as a result the ovary is unable to produce an egg
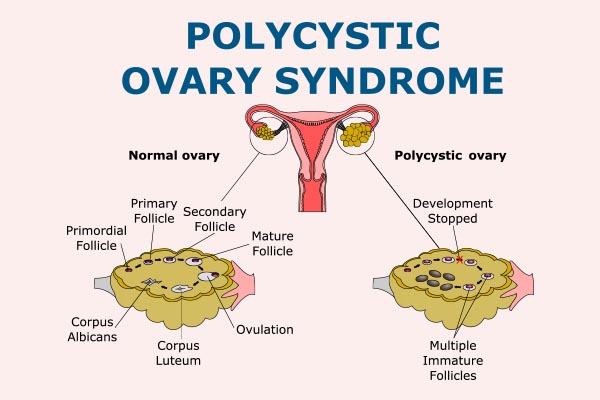
What is the difference between PCOD and PCOS?
PCOD/PCOS are similar in its nature, except syndrome means where other endocrine organs involvement is seen with accompanying diabetes, hypertension, obesity.
If disease is just limited to ovary, it is PCOD.
CAUSES of PCOS
Sedentary lifestyle is the major cause of PCOS. Many girls, right from an early age go through exam competition, long working hours due to homework, technology-based education, more machines for routine activities, less necessity for movement/exercise with the changes in society, urbanisation and migration to cities leading to adoption of a sedentary lifestyle.
An unhealthy, imbalanced or erratic diet (which has more of junk food, processed or refined ingredients), frequently eating such foods, irregular timings of food habits, fads of diets and supplements from unregulated sources seem to be contributing.
Stress can play a major part. In the current competitive world, globalization, the internet and dropping employment rates worldwide, women are dealing with jobs with high demand on performance, facing work pressure, family pressure. All these can also play a role.
Most important one is abnormal sleep pattern. Most people have inadequate sleep these days as they are active on phones, laptops, video games, work from home and even work from bed and are deprived of sleep.
Presence of chemical pollutants in body, through environmental pollution via air, water, food and skin absorption is considered as a contributing factor.
Genetic cause has not been proven yet. You can see that this was hardly there in previous generation women. What was different then was the hands-on, active, wholesome lifestyle and nutrition.
Symptoms
These are common complaints most people present to the clinic:
- Irregularities with their period: Irregular cycles, early or delayed cycle. May have scanty bleeding or prolonged bleeding.
- Weight Gain: Inspite of doing workouts still there is no loss of weight.
- Hair loss: Scalp hair loss mostly over front
- Male pattern body and facial hair: Excess of male hormones leads to thick facial hair, increased body hair.
- Difficulty in conceiving: Infertility now a days is becoming very common and one major reason is PCOD/PCOS.
How to diagnose this disease?
The criteria used to diagnose PCOS is universally known as Rotterdam criteria.
It includes
- Irregular periods- Patient can present with a menstrual cycle once in 2-3 months. When they bleed it will be scanty flow.
- Thick facial hair of over upper lip, chin, lower face, acne. Thick hair below umbilicus and midline over sternum. In PCOD, there is insulin resistance and it leads to a bulkier ovary and hence production of male pattern hormones in excess in the body leading to the excess hair.
- Ultrasound shows the evidence of PCOS. It is diagnosed by radiologist or gynaecologist by seeing the ovarian volume more than 10cc and multiple follicles in ovary (more than 12 to 20 in each ovary)
Complications of PCOS/PCOD:
- Most common complication of PCOS is infertility. Infertility in PCOS is mainly because of underlying ovulation problems. Women fail to ovulate regularly.
- Risk of diabetes and glucose intolerance are more in PCOS. It because of underlying insulin resistance. The hormonal disturbance in PCOS will result in imbalance between the ratios of good and bad cholesterol resulting in increased levels of bad cholesterol which in turn will increase the risk of hypertension & heart diseases.
- Associated symptoms like increased sugar levels, increased BP, increased cholesterol lead to development of stroke.
- There are chances of endometrial carcinoma due to hyperestrogen state due to PCOS
Treatment is as following:
- Diet modification
- This is very important to correct PCOD. One should eat a healthy diet containing more leafy vegetables, dry fruits etc.
- Avoid junk food & processed foods.
- Consume more fruits and vegetables than juices especially packaged ones.
- Avoid sugar (refined sugar, even honey and jaggery in moderation), chocolates.
- Switch to brown rice, oats, barley, millets as they are known to have lower glycemic index.
- Drink plenty of water around 2.5-3.5 liters per day.
- Lifestyle modification
- Physical activity for 1 hour per day makes our hormones normalise and complement each other and it reduces stress.
- Daily 10,000 steps/day walking. This is important.
- Cardiac workout 5 days/week (or) yoga for 1 hour which contains suryanamaskaras. Surya namaskaram are known to stimulate in a healthy way most of the endocrine organs of the body e.g. Pancreas, Thyroid.
- Medical treatments:
- To regularize cycles, for some women a 6 months course of Oral Contraceptive pills are prescribed.
- To correct hormone imbalance in PCOS we need to add tablets, which contains D-choroinositol and myoinositol, Vit D.
- In patients with infertility, for ovulation to occur, ovulation inducing drugs may be added and monthly follicular monitoring.
- Surgical treatments:
- PCOD can be controlled by laparoscopic ovarian drilling, this is the final intervention.