Arthritis and knee injury can limit the ability to extend and bend knees.
Over time, the deterioration or decline of the joint and surrounding tissue can make it difficult to perform the basic daily activities such as sitting and lying down. Total knee replacement surgery is a common solution for people who are facing knee deterioration after having taken conservative treatment in the form of medications, physiotherapy and other nonsurgical options. Total knee replacement or partial knee replacement provides the pain relief during movement, for more than 80-90 per cent of those who’ve undergone the surgery.
Most of these knee replacement procedures are done to replace knee joints damaged due to osteoarthritis. Total knee replacement surgery is considered one of the most effective as well as safest procedures in orthopaedics.
What is Knee Replacement Surgery?
Knee replacement surgery, also known as arthroplasty (Plasty- moulding, shaping), is a surgical procedure to repair a knee damaged by arthritis. This surgery may be considered for someone with severe arthritis or a severe knee injury.
During a knee replacement, a surgeon removes some cartilage and bone from the areas of the shinbone and thighbone, where they meet at the knee joint. The surgeon then replaces them with metal implant on both surfaces and a poly insert in between.. This gives both the bones of the knee joint smooth surfaces again so they can be easily flexed over each other.
What are the most common causes of knee replacement surgery?
Osteoarthritis:
This type of age-related arthritis is caused due to normal wear and tear of the knee joint. Osteoarthritis affects patients aged above 50 years due to more years of use, but younger people may have it too.
Osteoarthritis is caused by breakdown, inflammation, and the gradual and eventual loss of cartilage in the joints. When a person grows older the cartilage wears down and the bones rub together.
To compensate, these bones edges often grow thicker called osteophytes, which can further lead to more pain and friction.
Rheumatoid arthritis:
This is also known as inflammatory arthritis, the membrane around the knee joint to become thick and inflamed. Chronic inflammation damages the cartilage that leads to stiffness and soreness.
Post-traumatic arthritis:
This type of arthritis is after severe knee injury. When the bones around the knee break or ligaments tear, there is malalignment which will ultimately affect the knee cartilage.
What are the Types of Knee Replacement Surgery?
There are mainly two types of knee replacement surgery, total or partial.
Total Knee Replacement (TKR):
In TKR, the surgery mainly involves the replacement of both sides of the knee joint, which is the most common procedure.
The surgery lasts for approximately 2 hours. After the surgery and physiotherapy , the individual will have less pain and better mobility.
Partial Knee Replacement (PKR):
PKR is done only on one compartment of the knee joint most commonly done for medial or inner compartment. In this procedure, less bone is removed, so the incision is smaller, tissue handling is more localised.
PKR is suitable for those people with only one half of the knee is damaged. Post-operative rehabilitation is more straightforward and has less blood loss, lower risk of infection and blood clots.
Diet after a knee replacement surgery:
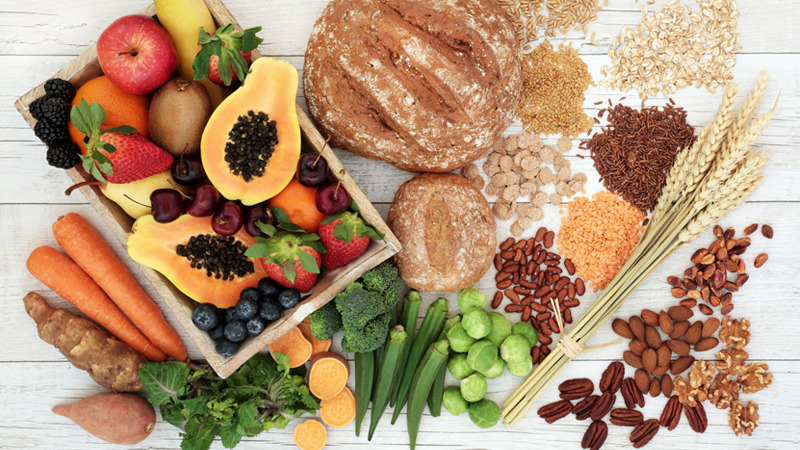
Eating good food which includes all the nutrients and protein is a very essential part of recovery. It will not only help you recover fast but will make you feel more energized. So, you can say that the food you consume will affect your well-being.
Include Lean protein
The most abundant protein in the body is collagen as it helps in getting tissue back together. Typically intake of protein should be around 0.8grams. But after a knee replacement surgery, you should increase this quantity. You should include at least 1.5 to 2.0 grams of protein. (If your weight is 68Kg then you should eat 102 to 136 grams of protein in one day. This means per meal it should be 25 to 30 grams and for two snacks 14 to 23 grams.)

Fibre
To feel energized all day long and concentrate on your work properly you should include soluble as well as insoluble fibre in your diet. Prunes are a very rich source of fibre, so you should eat a few of them each day. Some other food products are beans, legumes, apples, pears, bran flakes, oatmeal, and flax-seed meals. Given that moving around is limited in the first few weeks after surgery, constipation which may set in can be dealt with.
Bell peppers and Citrus Fruit
Vitamin C should be another essential part of your diet. For this, you should include bell pepper in the diet. (You will be surprised to know that one medium pepper contains 340 mg of Vitamin C). Especially if you have undergone the surgery which has a decent sized incision then this will really help the wound to heal faster. Other sources are guava, kale, citrus fruits, kiwi, and broccoli.

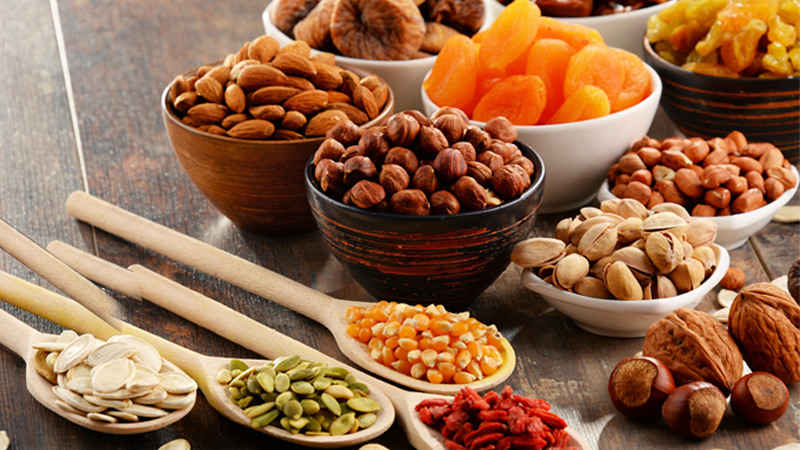
Nuts and seeds
Many seeds and nuts are excellent sources of zinc. Pumpkin, squash and sesame seeds contain zinc is very high amount and it helps the immune system to function properly. Moreover, it also helps in developing and activating the cells as well as promote cell growth. Oysters are considered as the highest concentration of zinc.

Pineapple & Papaya
Pineapple and papaya contain protease enzymes which help the body to digest proteins. These enzymes such as bromelain and papain help in reducing the swelling and inflammation. The problem is bromelain is found in the stem of the pineapple (that chewy part you do not eat!). Instead you should take a supplement like Bromelain with Quercetin which is also a great option.

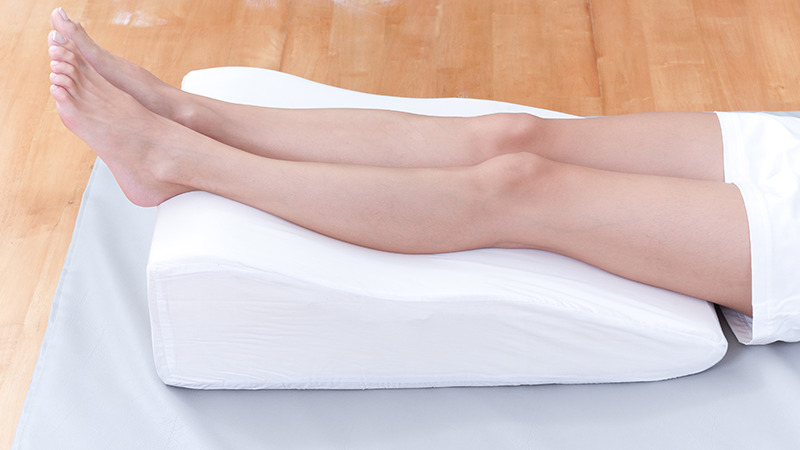
Recovery exercises for knee replacement surgery:
1. Rest and Elevate:
Lie on your back and elevate your leg using pillows when icing and doing ankle pumps.

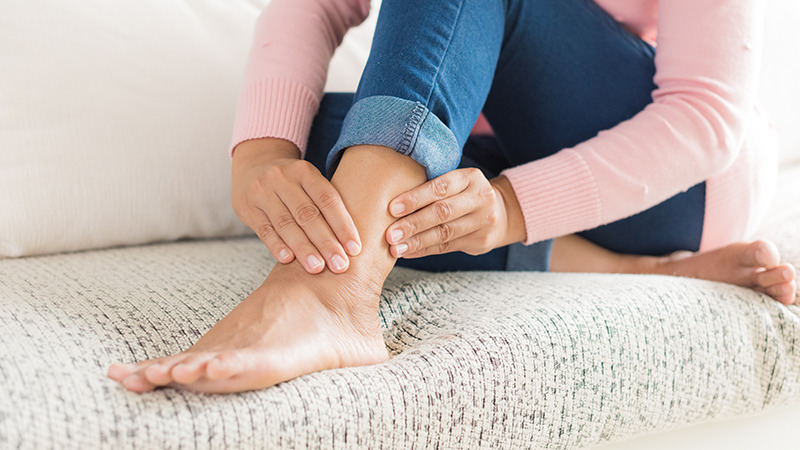
2.Ankle pumps and circles:
Pump your feet up and down by stretching your toes up toward you, then pushing your toes down away from you. In addition, rotate your feet at the ankle joint clockwise and counterclockwise.

3. Knee straightening stretch (sitting knee extension):
Sit on a sturdy chair with your leg straightened out in front of you, heel on an equal height chair or solid surface in front of you. Relax your leg and thigh muscles to let your knee straighten. You should feel a gentle stretch on the back of your knee. You can do thigh squeezes to increase the stretch.

4. Thigh squeezes (quadriceps sets):
Tighten the muscles on the front surface of your thigh by pushing the back of your knee down into the bed. Hold for 5 seconds and relax.
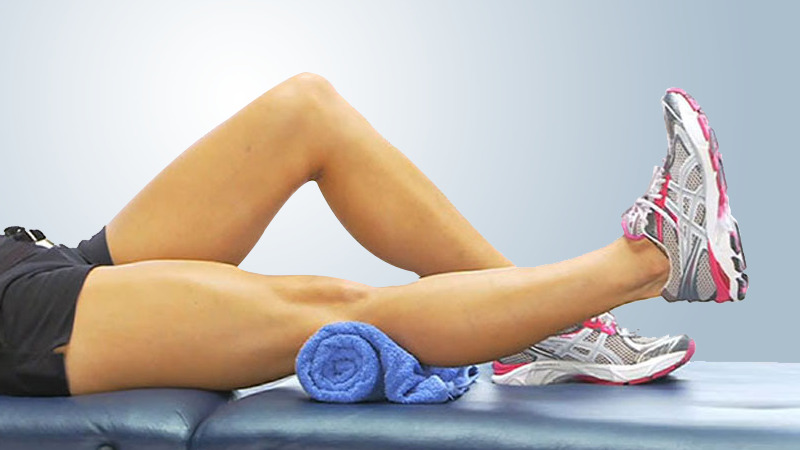

5. Heel slides (hip and knee flexion):
Bend your surgical hip and knee by sliding your heel up toward your buttocks while keeping your heel on the bed. Slide your heel back down to the starting position and relax. Keep your kneecap pointed up toward the ceiling during the exercise. You may want to use a plastic bag under your heel to help it slide easier.
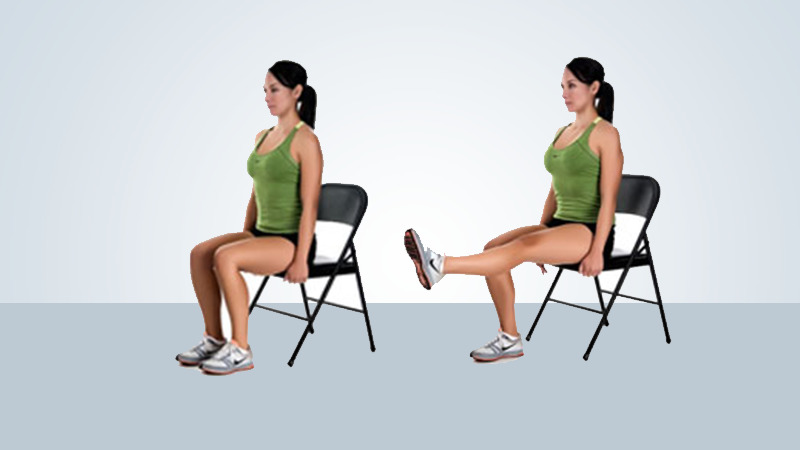
6. Leg slides (abduction/adduction):
Slide your surgical leg out to the side, keeping your kneecap pointed up toward the ceiling. Slide your leg back to the starting position. You may want to use a plastic bag under your heel to help it slide easier.
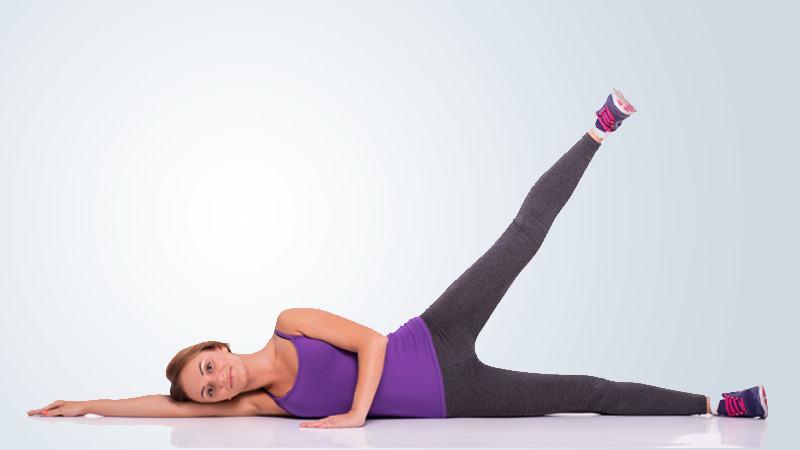

7. Straight leg raises:
Bend your non-surgical leg with your foot flat on the bed. Tighten the muscles on the top of your thigh, stiffening your knee. Raise your surgical leg up (about 12 inches), keeping your knee straight. Work up to holding for 5 seconds.
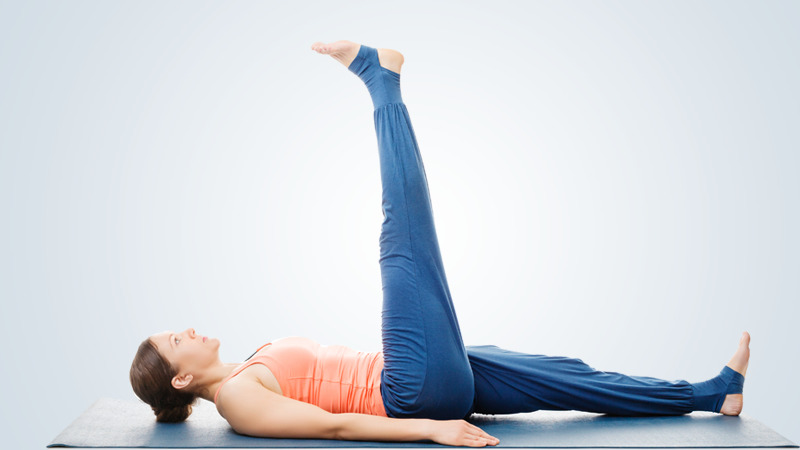

8. Sitting kicks (long arc quadriceps):
Sit on a sturdy chair or on the side of your bed. Straighten your knee. Work up to holding for 5 seconds.
Zoi Hospital’s orthopaedic department might be your best option for treatment
In Zoi’s orthopaedics and traumatology department, each of our orthopaedic doctors is an expert in a specific area of orthopaedics, which means that you will always receive individualized care and specialized treatment.
The Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology specialises in handling accident and trauma cases, joint and bone diseases and sports injuries that require advanced surgical procedures and physiotherapy for a complete repair and rehabilitation.
Our orthopedic surgeons perform a variety of procedures including knee ligament tear surgery (with the most common being ACL repair surgery), partial and total knee replacement, total hip replacement, shoulder injury repair surgery and spine surgery (especially minimally invasive techniques), all of which are performed by some of the best orthopaedic surgeons in Hyderabad.
Zoi hospitals is among the few hospitals to perform computer navigation assisted knee replacement. The advantage of using computer navigation is the precision of cuts and implant placement which allows for early rehabilitation and increases longevity of the prosthesis.
At Zoi Hospitals, after completion of the procedure, you will be under the care of an intensivist, operating orthopaedic surgeon, physical therapist and dietician. Pain control measures are started immediately and gradual rehabilitation towards recovery is supervised by the team to ensure that you are discharged in a stable condition by the end of the third or fourth day of your hospital stay.
Procedure Time: 1 – 3 hours
Postprocedure Care: 1 – 5 days
Procedure Cost: Varies depending on the type of implants and use of computer navigation system.
Back to Work: 4 – 6 weeks
At Zoi orthopaedic hospital, we don’t just provide orthopaedic treatment, we make sure that you get back in action as soon as possible.

